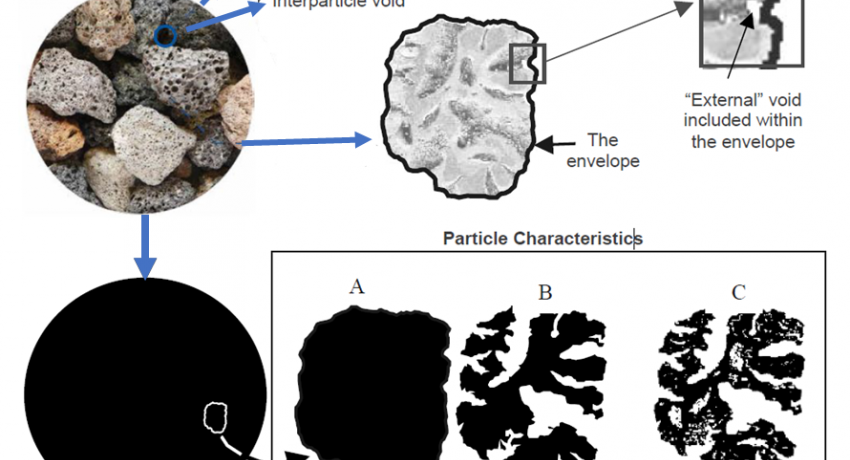
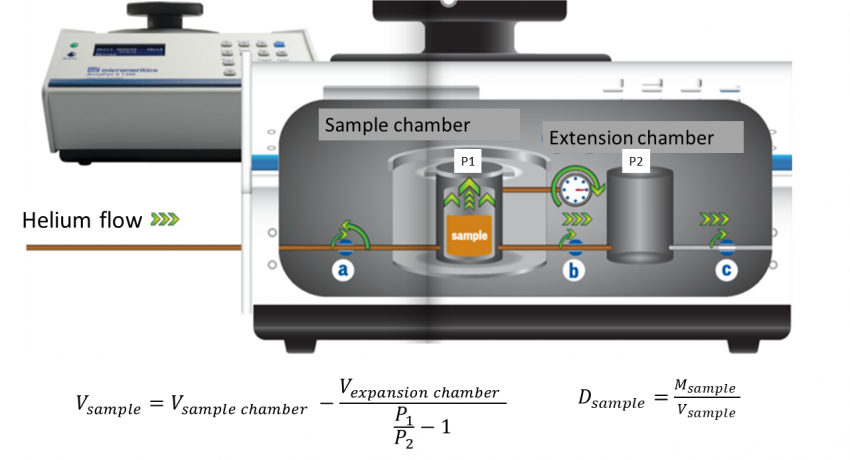
There are two types of density associated with powders. Envelope (or bulk) density is determined for porous materials when pore space spaces within material are included in the volume measurement. Skeletal density is the ratio of the mass of solid material to the sum of the volumes of the solid material and closed (or blind) pores within the material (ASTM D3766). Micromeritics Accupyc II 1340 measures the skeletal volume of a material by gas displacement using the volume-pressure relationship of Boyle’s Law. An inert gas, typically helium, is used as the displacement medium. The sample is placed in a sealed cup of a known volume. This cup is then placed into the sample chamber. Gas is introduced to the sample chamber and then expanded into a second empty chamber with a known volume. The pressure observed after filling the sample cell and the pressure discharged into expansion chamber are measured, and then the volume is calculated. The density is determined by dividing the sample weight by the volume measured. The density measured by Helium Pycnometry is often referred to as “helium density” implying that open pores excluded in the calculation. Since He cannot access closed pores, they are included into the total volume.
Illustration of various volume types. Source: Paul Webb (2001) Volume and Density Determinations for Particle Technologies.
Measurement principle of He Pycnometer.
- 10-cc cell volume (1.80 cm ID x 3.93 cm D (0.72 in. ID x 1.55 in. D.) contains 1- and 3.5-c sample cups.
- Cups dimensions: 1 cc volume - 1.2 cm diameter x 1.1 cm height; 3.5 cc volume – 1.7 cm diameter x 1.7 cm height.
- The sample can be a powder or bulk. Bulk sample must fit in the sample cup.
- Sample needs to fill at least two-third of a cup for a quality result.
- Precision: reproducibility typically to within ±0.01% of the nominal full-scale cell chamber volume. Reproducibility guaranteed to within ± 0.02% of the nominal full-scale volume on clean, dry, thermally equilibrated samples using helium in the 15 to 35ºC range.
- Accuracy: accurate to within 0.03% of reading, plus 0.03% of sample capacity.
- Pharmaceuticals –polymorphic, hydrated, and amorphous forms of products, as well as purity, can be determined by comparing measured density with theoretical and historical values.
- Coatings – dried film density can be used in determination of Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) content of clear and pigmented coatings.
- Calcination – different crystal structures of carbon and ceramic undergo structural rearrangement through pressure or temperature treatment resulting in different densities.
- Ceramics and powder metallurgy – if density of the finished part is significantly less than that of the constituent powder, closed pores have formed during the part processing.
- Rigid cellular plastics – foams exhibit different properties based upon the ratio of open and closed cells determined from density.
- Plastic films – density can be used to determine the quantity of entrapped air and degree of crystallinity.
- Slurries – the quantity of liquid in a slurry mixture can be calculated by measuring the density of the slurry.
- Organic chemicals and polymers –polymerization and organic reforming processes are used to produce desired compounds from raw materials. Conversion and purity can be monitored by comparing measured density to theoretical density of the desired product.
- Blending of materials – accuracy and reproducibility of the blend can be monitored by comparing the measured densities to the expected density based upon the target recipe of primary ingredients.