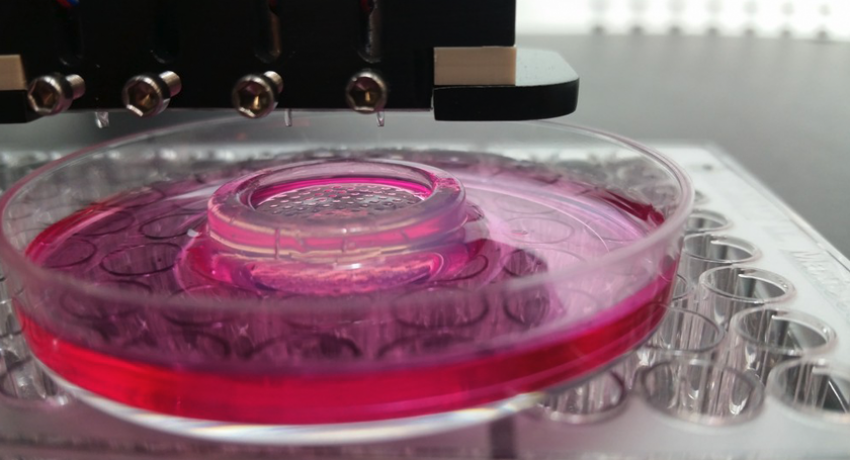
Engineering Faculty Member Receives Grants Totaling $1.5M For Bioprinting
Ibrahim Tarik Ozbolat, has received four grants totaling about $1.5 million to explore ways to bioprint biological tissues like bone, lungs and other organs for use as models in a variety of studies.