Biosensing platform simultaneously detects vitamin C and SARS-CoV-2
By Mariah Lucas
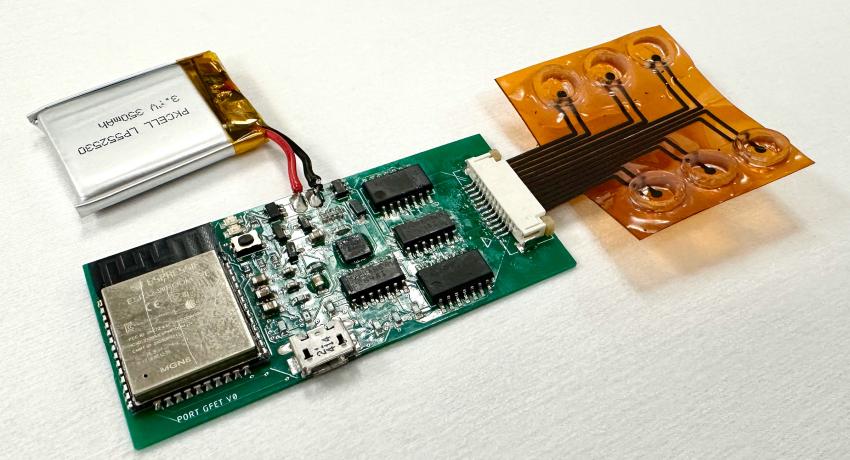
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — In the COVID-19 pandemic era, at-home, portable tests were crucial for knowing when to wear a mask or isolate at home. Now, Penn State engineering researchers have developed a portable and wireless device to simultaneously detect SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, and vitamin C, a critical nutrient that helps bolster infection resistance, by integrating commercial transistors with printed laser-induced graphene.
Getting over the hump to improve fuel cell manufacturing
By Sarah Small
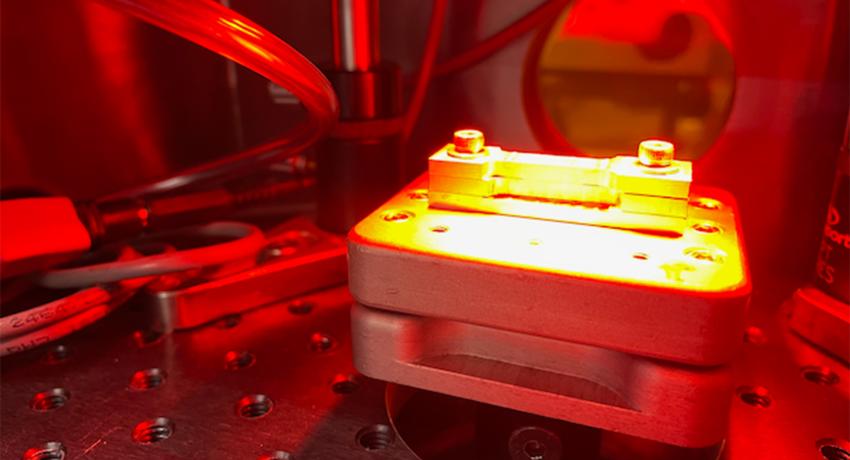
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Fuel cells offer a form of clean energy across many sectors and are of particular interest in vehicles, where they produce no emissions. The production of fuel cells requires the use of a rapid laser welding process; however, welding at too high a speed results in humping, marked by surface irregularities on the weld seam.
Q&A: $2.5M grant to help reduce emissions, inefficiencies in industrial systems
By Sarah Small
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A team led by researchers at Penn State recently received a $2,491,443 grant from the Department of Energy’s (DOE) Industrial Efficiency and Decarbonization Office (IEDO) to reduce emissions and increase thermal efficiency in industrial systems. The team, which includes researchers at Saint-Gobain Ceramics & Plastics Inc., plans to achieve these goals by developing a new ceramic heat exchanger.
Graduate student’s materials science research recognized by national society
By Jamie Oberdick
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Mingyu Yu, doctoral candidate in materials science and engineering at Penn State, recently received the Graduate Student Research Award from the professional society AVS: Science and Technology of Materials, Interfaces and Processing for innovative research in two-dimensional materials.
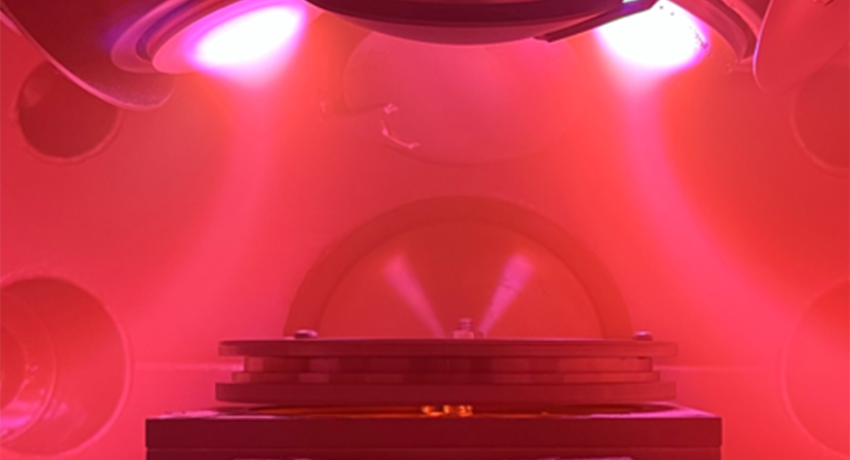
Proximity effect: Method allows advanced materials to gain new property
By Matthew Carroll
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Ferroelectrics are special materials with polarized positive and negative charges — like a magnet has north and south poles — that can be reversed when external electricity is applied. The materials will remain in these reversed states until more power is applied, making them useful for data storage and wireless communication applications.
Brian Fronk
(e) bmf141@psu.edu
(o) 814 863 8997
229 Reber Building