Study reveals new clues about how 'Earth's thermostat' controls climate
By Matthew Carroll
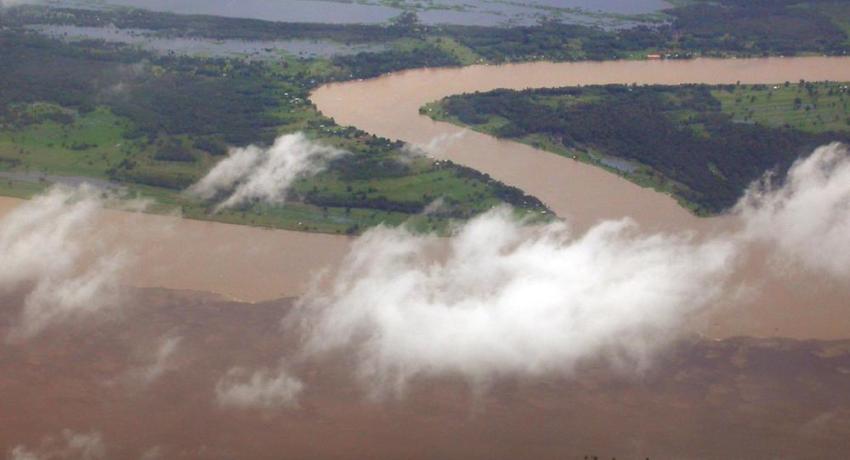
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. – Rocks, rain and carbon dioxide help control Earth’s climate over thousands of years — like a thermostat — through a process called weathering. A new study led by Penn State scientists may improve our understanding of how this thermostat responds as temperatures change.