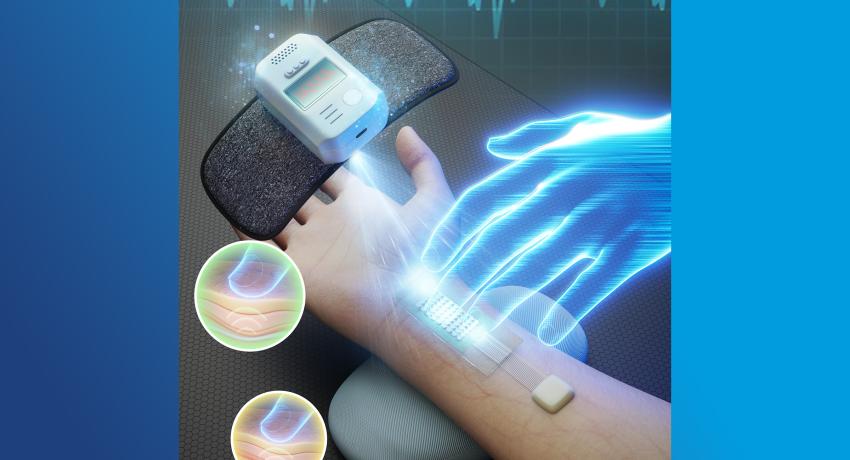
Breaking a sweat: Using chloride in sweat to help diagnose cystic fibrosis
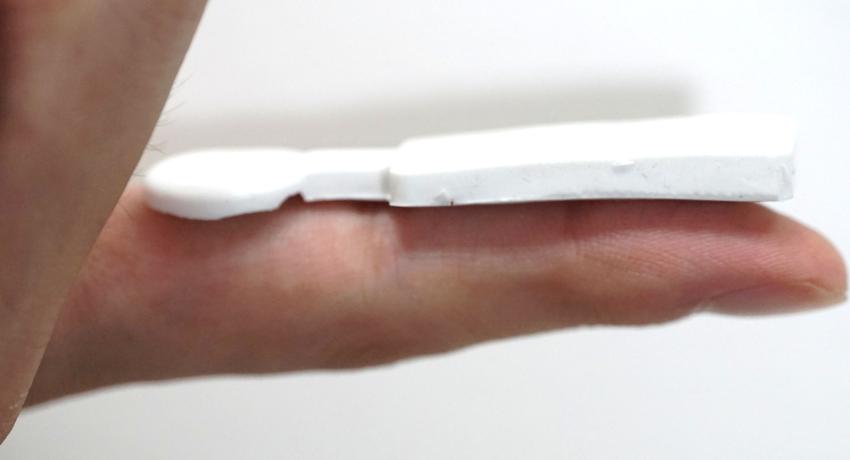
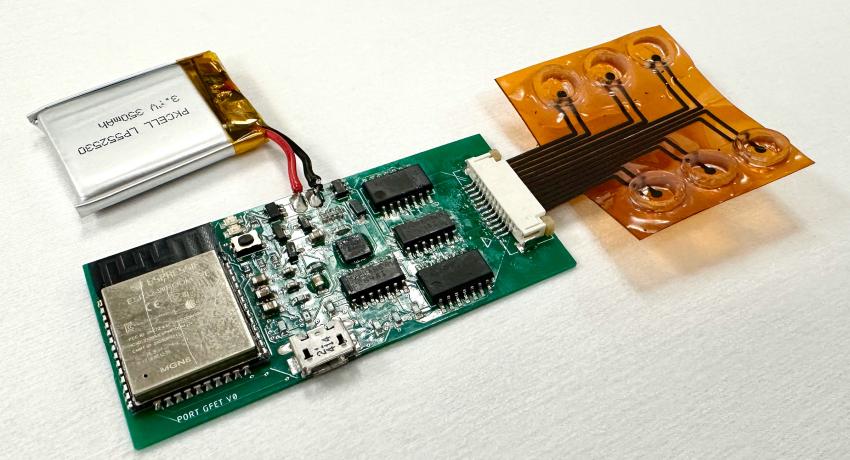
A group of researchers at Penn State recently developed a wearable device capable of accurately tracking chloride ion levels in sweat, which is essential for evaluating hydration status and health conditions like cystic fibrosis and more.